Heartbeat Mechanism
The heartbeat mechanism is the basis for service registration in service governance. Below is the class diagram of the heartbeat mechanism:
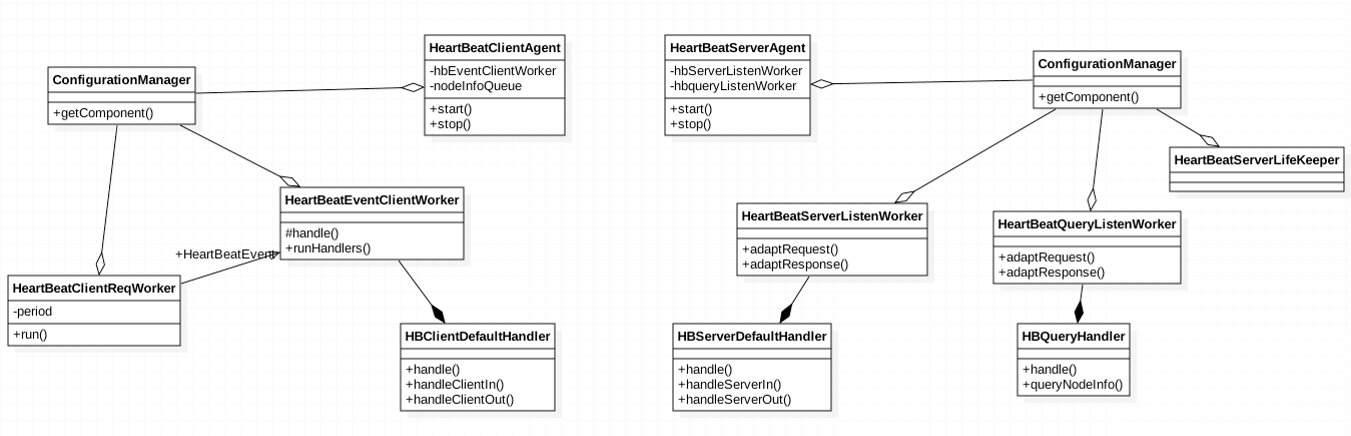
As shown above, there are both client heartbeat mechanism and server heartbeat mechnism.
The client heartbeat mechanism generates the contents of heartbeat messages and send the messages to the server every 15 minutes by default via Http.
Message contents:
- Modules and Http servers started by the MSCP node;
- Context data: OS information, JDK information and disk use;
- Context performance data: CPU, memory, conncetion count, port traffic and disk IO. Client life cycle: Alive (1*TTL, green) —> Dying (2*TTL, red) —> Dead (5*TTL, grey)—> Disappear (10*TTL)
The server heartbeat mechanism stores the contents of the heartbeat messages and handles the cascading with the multi-level service registration center. Storage: CacheManager hash structure:
node.info: key: NodeInfo.id, value: NodeInfo JSONCascading: multi-level service registration center. Some business scenarios have low tolerance with the update latency of the service registration information, which requires the computational node of the heartbeat cascading to be a service registration center.